Aliases¶
Aliases are named lists of networks, hosts or ports that can be used as one entity by selecting the alias name in the various supported sections of the firewall. These aliases are particularly useful to condense firewall rules and minimize changes.
Aliases can be added, modified and removed via .
Alias Types¶
OPNsense offers the following alias types:
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
Hosts |
Single hosts by IP or Fully Qualified Domain Name or host exclusions (starts with “!” sign) |
Networks |
Entire network p.e. 192.168.1.1/24 or network exclusion eg !192.168.1.0/24 |
Ports |
Port numbers or a port range like 20:30 |
MAC addresses |
MAC address or partial mac addresses like
|
URL (IPs) |
A table of IP addresses that are fetched once |
URL Tables (IPs) |
A table of IP addresses that are fetched on regular intervals. |
GeoIP |
Select countries or whole regions |
Network group |
Combine different network type aliases into one |
External (advanced) |
Externally managed alias, this only handles the placeholder. Content is set from another source (plugin, api call, etc) |
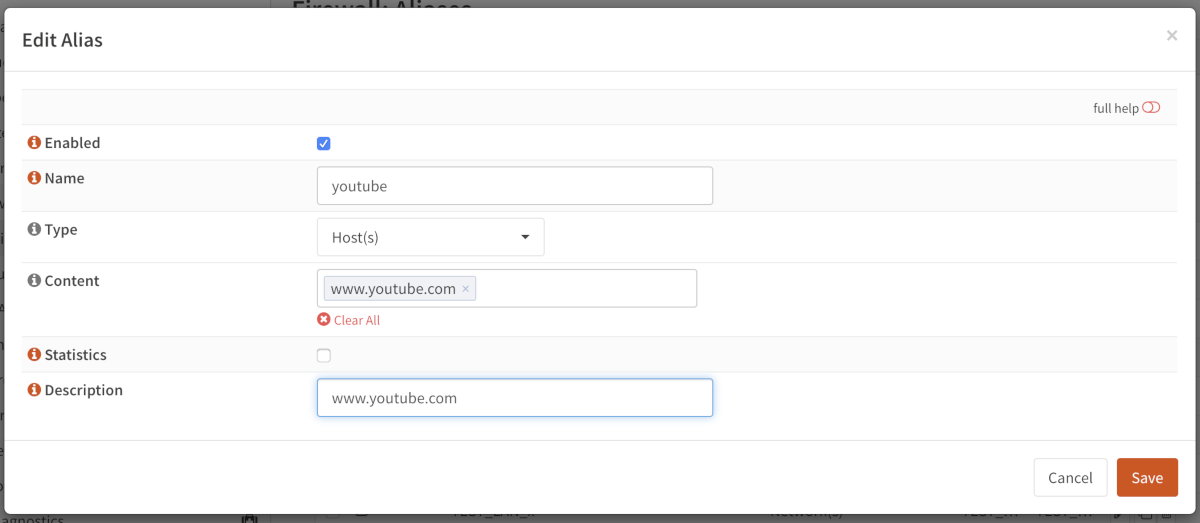
Hosts¶
Hosts can be entered as a single IP address or a fully qualified domain name. When using a fully qualified domain name, the name will we resolved periodically (default is each 300 seconds).
Apply changes and look at the content of our newly created pf table.
Go to and select our newly created youtube table.
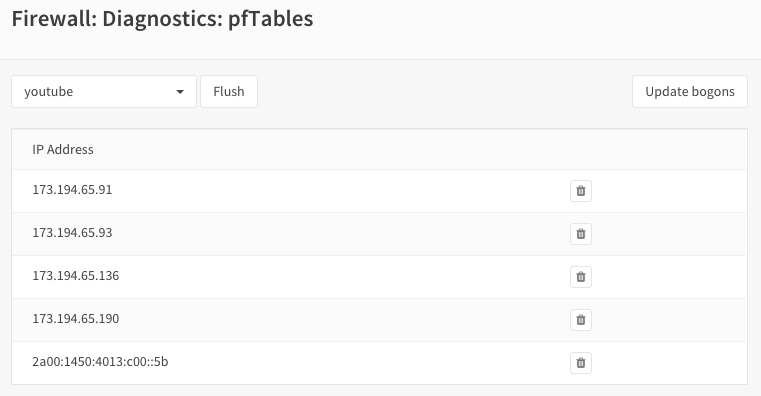
As you can see there are multiple IP addresses for this domain.
Tip
To change the alias domain resolve interval, go to and set Aliases Resolve Interval to the number of seconds to refresh.
Hosts type Aliases can contain exclusion hosts. Exclusion addresses starts with “!” sign (eg !192.168.0.1) and can be used to exclude hosts from Network Group Aliases.
Warning
Please note thet the Flush action is not persistent!
“flush” means flush the current contents of the alias, which will be repopulated when it’s not an external type, so flush in most cases isn’t very useful.
Same behaviour applies to the API call alias_util flush
Networks¶
Networks are specified in Classless Inter-Domain Routing format (CIDR). Use the the correct CIDR mask for each entry. For instance a /32 specifies a single IPv4 host, or /128 specifies a single IPv6 host, whereas /24 specifies 255.255.255.0 and /64 specifies a normal IPv6 network. Network type Aliases can contain exclusion hosts or networks. Exclusion addresses starts with “!” sign (eg !192.168.0.0/24) and can be used to exclude hosts or networks from current Alias or Network Group Alias
Ports¶
Ports can be specified as a single number or a range using a colon :. For instance to add a range of 20 to 25 one would enter 20:25 in the Port(s) section.
MAC addresses¶
Hardware mac addresses can be specified as a (partial) hex value, such as F4:90:EA to match all addresses from
Deciso or f4:90:ea:00:00:01 to match a single item (the input is case insensitive).
The way these aliases function is approximately the same as hostnames in host type aliases, they are resolved on periodic
intervals from the arp and ndp tables.
Warning
Please be aware that hardware addresses can be spoofed (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MAC_spoofing), which doesn’t make filters on them more secure than ip addresses in any way.
Note
Since mappings between addresses and mac addresses are resolved periodically the actual situation can differ, you can always check to inspect the current contents of the alias.
URL Tables¶
URL tables can be used to fetch a list of IP addresses from a remote server. There are several IP lists available for free, most notably are the “Don’t Route Or Peer” lists from Spamhaus.
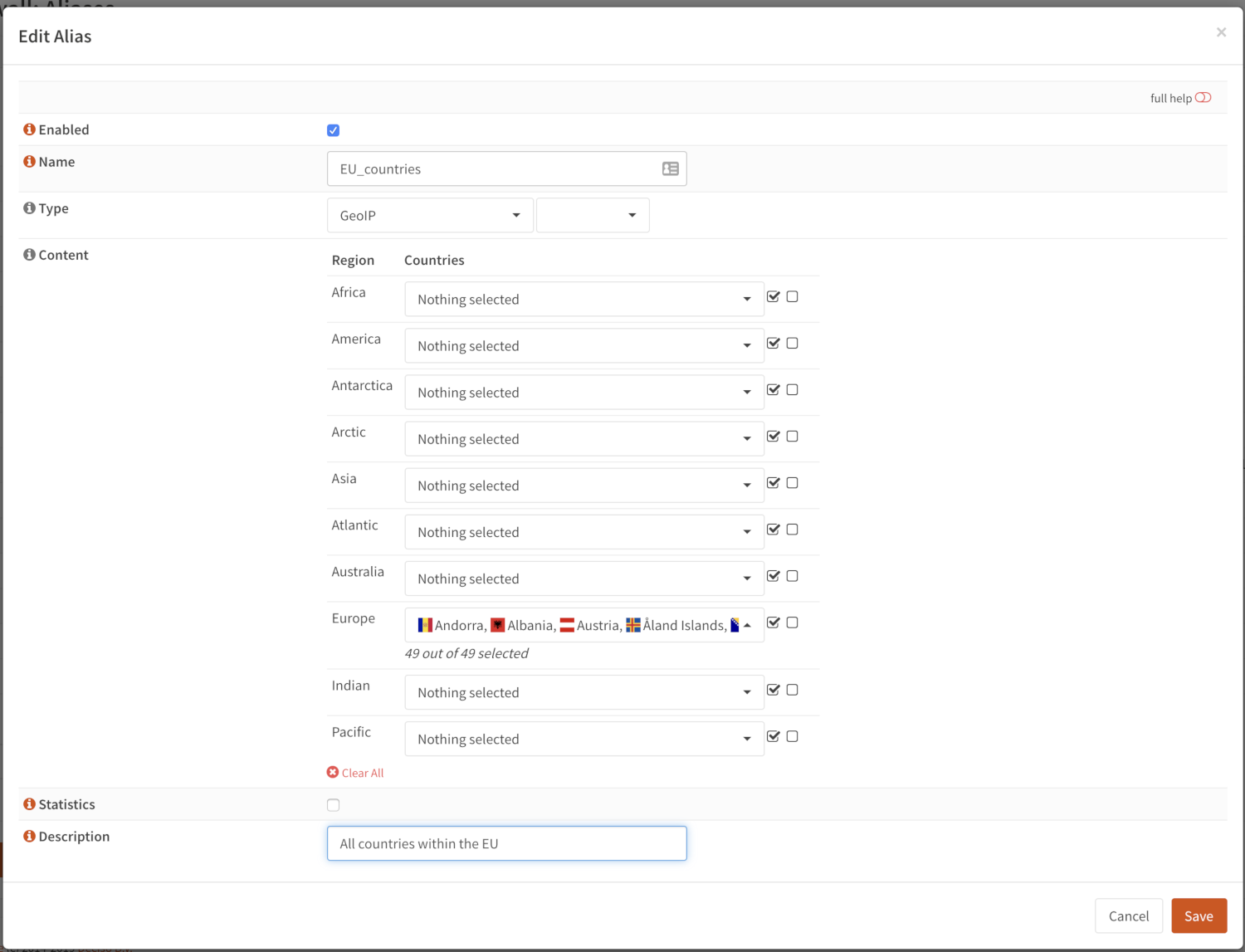
GeoIP¶
With GeoIP alias you can select one or more countries or whole continents to block or allow. Use the toggle all checkbox to select all countries within the given region.
To use GeoIP, you need to configure a source in the tab, the most commonly used source is MaxMind, for which we have a how-to available : MaxMind GeoIP’s Setup
The configured url should point to a zip file containing the following csv files:
Filename |
Purpose |
Format |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
%prefix%-locations-en.csv |
maps geo locations to iso countries |
geoname_id,,,,country_iso_code |
1,,,,NL |
%prefix%-IPv4.csv |
IPv4 networks |
network,geoname_id |
2.21.241.0/28,1 |
%prefix%-IPv6.csv |
IPv6 networks |
network,geoname_id |
2001:470:1f15:210::/64,1 |
The %prefix% can be used to identify the product and/or vendor, in MaxMind’s case these files are named
GeoLite2-Country-Locations-en.csv, GeoLite2-Country-Blocks-IPv4.csv, GeoLite2-Country-Blocks-IPv6.csv for example.
Tip
Geo ip lists can be rather large, especially when using IPv6. When creating rules, always try to minimize the number of addresses needed in your selection. A selection of all countries in the world not being the Netherlands can usually be rewritten as only addresses from the Netherlands for example.
Tip
If the number of items is larger than the allocated alias size, you can assign more memory to aliases.
Network group¶
Combine different network type aliases into one, this type of alias accepts other host type aliases (networks, hosts, …).
Although nesting is possible with other alias types as well, this type only displays valid aliases easing administration, functionally
a Networks type alias can do the same but uses a different presentation.
External¶
The contents for external alias types is not administered via our normal alias service and can be practical in scenarios where you want to push new entries from external programs. Such as specific lockout features or external tools feeding access control to your firewall.
In you can always inspect the current contents of the external alias and add or remove entries immediately.
Tip
When changing alias contents which are used on firewall rules with state tracking enabled, you might need to remove the specific state before the new rule turns active. (see )
Tip
Since external alias types won’t be touched by OPNsense, you can use pfctl directly in scripts to manage
its contents. (e.g. pfctl -t MyAlias -T add 10.0.0.3 to add 10.0.0.3 to MyAlias)
Using Aliases in pf Firewall Rules¶
Aliases can be used in firewall rules to ease administration of large lists. For instance we might need a list of remote IP addresses that should have access to certain services, when anything changes we only need to update the list.
Let’s create a simple alias to allow 3 remote IP addresses access to an ipsec server for a site to site tunnel connection:
192.168.100.1
192.168.200.2
192.168.202.2
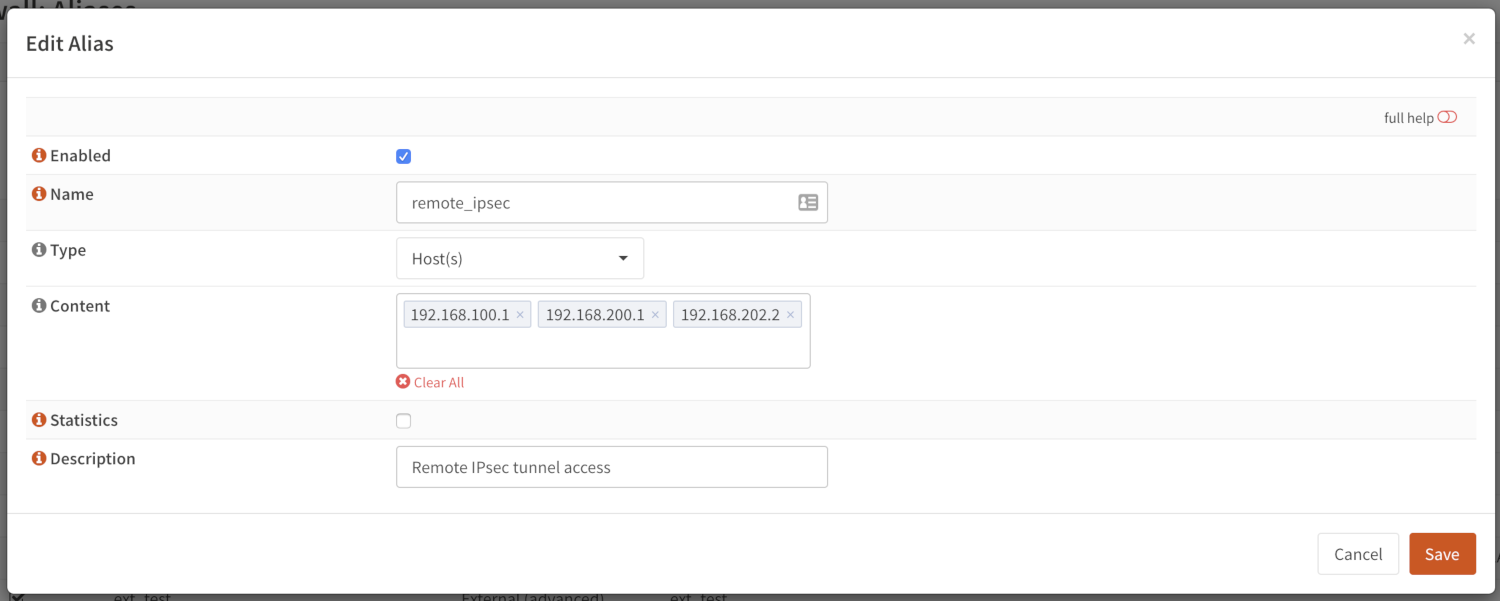
We call our list remote_ipsec and update our firewall rules accordingly.
Note
The list icon identifies a rule with an alias.
Export / Import¶
The alias admin page () contains a download and an upload button in the footer of the table, with this feature you can
merge aliases into the configuration and download a json formatted list of all aliases in the system.
Since data is validated before insertion, it shouldn’t be possible to import defective data (if the import fails, a list of errors is presented).
Tip
When performing migrations, sometimes its easier to change multiple items at once in a text editor. This feature can easily be used to facilitate that, with limiting risk of a broken configuration (since items are validated equally as single item input would do).
Add new entries using our API¶
The endpoints from the alias_util can easily be used to push new entries into an alias (or remove existing ones). In case of an external alias these items won’t be persistent over reboots, which can be practical in some use-cases (large frequent changing lists for example).
The document “Use the API” contains the steps needed to create an api key and secret, next you can just call the same endpoint the user interface would.
Below you see how to add 10.0.0.2 to an alias named MyAlias using an insecure connection (self-signed cert) on
the host opnsense.firewall with curl. The verbose option provides more details about the data exchanged between the
two machines.
curl \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--basic \
--user "key:secret" \
--request POST \
--insecure \
--verbose \
--data '{"address":"10.0.0.2"}' \
https://opnsense.firewall/api/firewall/alias_util/add/MyAlias
Note
Adding aliases using /api/firewall/alias_util/add/ is only supported for Host, Network and External type aliases
Exclusions¶
Pf firewall tables support exceptions (or exclusion) of addresses. This feature can be used in one Alias or in combined (Network group type) Aliases. See (https://www.freebsd.org/doc/handbook/firewalls-pf.html 30.3.2.4).
Nesting¶
For host and network alias types nesting is possibility, this can simplify management a lot since single items can be named properly and grouped into sections for administration.
For example, we define 4 servers among 2 critical using different rulesets:
server_a {10.0.1.1}
server_b {10.0.1.2}
server_c {10.0.1.100}
server_d {10.0.1.200}
critical_servers {server_a , server_b}
other_servers {server_c , server_d}
servers { critical_servers , other_servers}.
The alias servers will contain all 4 addresses after configuration.
There is also a possibility to combine different Aliases with Aliases, consisting of exclusions. For example, there is Alias “FireHOL” that use extensive externl drop-list and two Aliases that contains subnet and hosts exclusions. It is possible to create Network group (combined) Alias (“FireHOL_with_exclusions”):
FireHOL {https://raw.githubusercontent.com/firehol/blocklist-ipsets/master/firehol_level1.netset}
subnets_exclusions {!127.0.0.0/8, !0.0.0.0/8}
hosts_exclusions {!8.8.8.8}
FireHOL_with_exclusions {FireHOL, subnets_exclusions, hosts_exclusions}
FireHOL_with_exclusions Alias will contain all records from FireHOL Alias excluding addresses from exclusions Aliases.
It’s always good to check if an address is included in the Alias via
Spamhaus¶
The Spamhaus Don’t Route Or Peer Lists DROP (Don’t Route Or Peer) and EDROP are advisory “drop all traffic” lists, consisting of netblocks that are “hijacked” or leased by professional spam or cyber-crime operations (used for dissemination of malware, trojan downloaders, botnet controllers). The DROP and EDROP lists are a tiny subset of the SBL, designed for use by firewalls and routing equipment to filter out the malicious traffic from these netblocks.
Source : https://www.spamhaus.org/drop/
- Downloads
To setup the DROP and EDROP lists in combination with the firewall rules, read: Configure Spamhaus (E)DROP